Heat Transfer Technology in Advertising Production
June 11, 2025
Heat transfer is a widely used printing technique in the advertising industry, leveraging the principles of heat transfer to imprint patterns, text, or images onto various advertising mediums.
- Steps of Heat Transfer Process

The working principle of heat transfer in advertising is primarily based on sublimation. The process can be summarized into the following steps:
1. Preparation
First, design the pattern, text, or image according to advertising requirements, ensuring vibrant colors and clear details. Then, prepare the transfer materials (such as heat transfer paper or film) and the substrate (such as fabric, metal, or plastic). The transfer material is pre-printed with the design and coated with a special heat-sensitive adhesive layer.
2. Heating and Transfer
Use a heat transfer machine or similar equipment to heat the transfer material. During heating, the heat-sensitive adhesive layer softens and releases the color components of the pattern. As the temperature rises, the color components (mainly dyes) transition directly from a solid to a gaseous state. These gaseous dyes are then absorbed and solidified on the substrate surface, forming a durable pattern.
3. Cooling and Setting
After the heating process, the substrate needs to be cooled to ensure the pattern adheres firmly to the surface. Once cooled, the pattern integrates seamlessly with the substrate, creating a vivid and realistic advertising effect.
II. Applications of Heat Transfer Technology
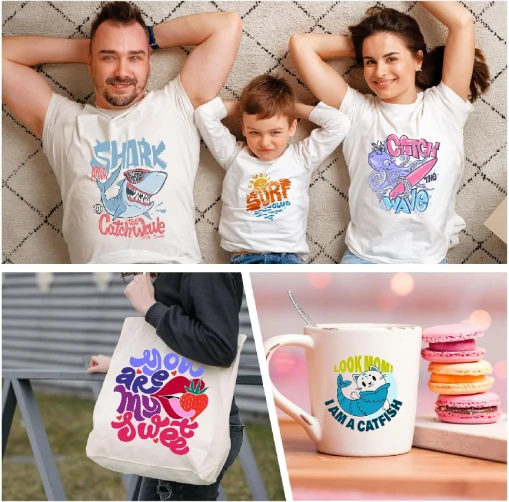

1. Advertising Promotional Materials
– Heat transfer technology can quickly imprint vibrant, high-resolution patterns and text onto paper, fabric, or other materials, producing eye-catching posters and banners for indoor or outdoor advertising campaigns.
– For flyers, product brochures, and other printed materials, heat transfer ensures bright and clear patterns and text, enhancing promotional effectiveness.
2. Personalized Gift Customization
– Heat transfer is commonly used for customizing clothing and accessories such as T-shirts, caps, and backpacks, imprinting unique patterns, text, or images to meet consumer demand for personalization.
– It is also applied to home items like mugs, tableware, and cushions, adding aesthetic appeal and interestingness through personalized designs.
3. Outdoor Signage and Wayfinding Systems
– Heat transfer technology produces durable and vibrant outdoor billboards for advertising in public spaces such as city streets and commercial plazas.
– In public venues like airports, hospitals, and shopping malls, heat transfer is used to create wayfinding signs, such as directional boards and floor indexes, providing clear guidance to the public.
4. Industrial Manufacturing and Product Labeling
– In industrial production, heat transfer is used to create product labels, barcodes, and safety signs, ensuring accurate and traceable product information.
– For industrial products like machinery and instruments, heat transfer is employed to imprint brand logos, model specifications, and other identifiers, enhancing professionalism and brand image.
III. Key Considerations in Heat Transfer Operations
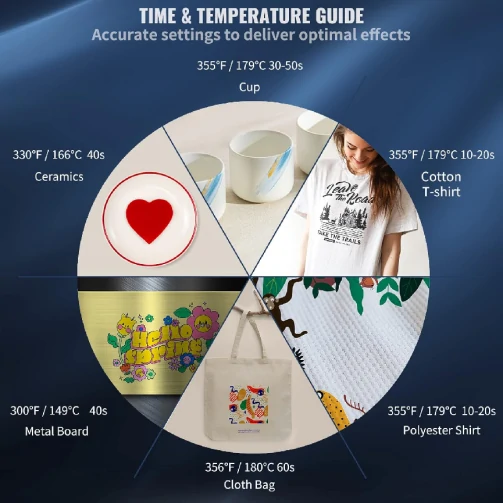
As a common printing technique, heat transfer requires attention to several aspects to ensure optimal results and quality.
1. Material Selection and Preparation
– Choose the appropriate heat transfer paper or film based on the substrate material to ensure smooth transfer and strong adhesion with durability.
– Ensure the transfer materials are free from defects or damage to avoid compromising the transfer effect.
2. Equipment and Temperature Control
– Before using the heat transfer machine, ensure it is in good working condition and perform necessary Commissioning and calibration.
– Precisely control the temperature of the heat transfer machine to avoid incomplete transfer or damage to the substrate due to excessive or insufficient heat. The optimal transfer temperature depends on the characteristics of the transfer material and substrate.
3. Operational Process
– Ensure accurate alignment between the pattern and the substrate during transfer to prevent misplacement or bias.
– Apply even pressure during the transfer process to ensure uniform patterns imprinting, avoiding blurred or mutilate results.
4. Safety and Protection
– Heat transfer involves high-temperature operations, so keep flammable materials away and ensure proper ventilation in the workspace.
– Avoid direct contact with high-temperature components to prevent burns.
– Ensure the electrical components of the heat transfer machine are properly connected to prevent electrical faults or accidents.
.png)
.png)
.png)
